
It is an expansion of the valence bond theory.īefore the formation of the atomic orbitals, they have different energies, but after the formation, all the orbitals have the same energy. The orientation of these orbitals determines the geometry of the molecule. Hybridization is the formation of hybrid orbitals by mixing two or more atomic orbitals.
Hybridization theory is a technique we use to describe the orbital structure of a molecule.

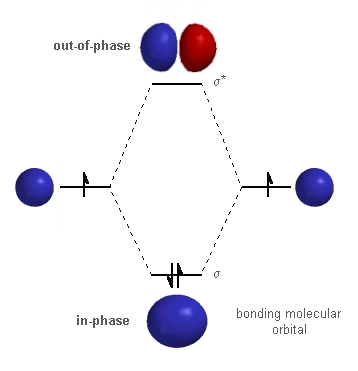
Thus, this description briefly explains the basis of the molecular orbital theory. We can use this theory to describe the structure of complicated molecules to explain why some molecules don’t exist (i.e. If we consider a sigma bond, the denotation for bonding orbital is σ, and the anti-bonding orbital is σ*. The bonding orbital has lower potential energy than the anti-bonding orbital. Rather, these electrons actively oppose the formation of the chemical bond. The bonding electrons occupy the bonding orbital while the electrons in the anti-bonding orbital do not participate in bond formation. Here, the in-phase combination of the two atomic orbitals makes the bonding orbital while out-of-phase combination forms the anti-bonding orbital. Then we need to find the missing orbital.
#In phase combination of atomic orbitals free#
But according to quantum mechanics, they are free to change the shape but need to have the same number of orbitals. When orbitals interact with each other, they tend to change their shapes accordingly. Here, we can start with two orbitals of two atoms and end up with one orbital (the molecular orbital) which belongs to both atoms.Īccording to quantum mechanics, atomic orbitals cannot appear or disappear as we wish. However, if the requirements are fulfilled and a chemical bond forms between two atoms, then the corresponding orbitals involved in bonding are called molecular orbitals.

If not, the electrons will be in the “anti-binding region” which will help the repulsive force between the atoms. Here, the electrons must exist in a region called “binding region”, to form this chemical bond. Basically, this means, the attractive forces between two atoms should be higher than the repulsive forces between those two atoms. A chemical bond forms between two atoms when the net attractive force between two atomic nuclei and the electrons in between them exceeds the electrostatic repulsion between two atomic nuclei. Let us discuss this theory in detail.įirst, we need to know what molecular orbitals are. It is the most productive way of explaining chemical bonding in molecules.

Molecular orbital theory is a technique of describing the electronic structure of molecules using quantum mechanics. Summary What is Molecular Orbital Theory? Side by Side Comparison – Molecular Orbital Theory vs Hybridization Theoryĥ. The most acceptable theory among them is the molecular orbital theory. VSEPR theory, Lewis theory, valence bond theory, hybridization theory and molecular orbital theory are such important theories. There are different theories developed to determine the electronic and orbital structures of molecules. The key difference between molecular orbital theory and hybridization theory is that molecular orbital theory describes the formation of bonding and anti-bonding orbitals, whereas hybridization theory describes the formation of hybrid orbitals.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
